By Madison Lozano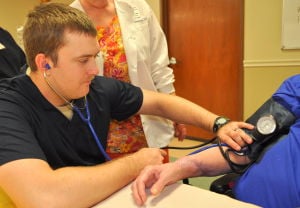 Sgt. Angela Hughes was always interested in nursing, but wasn’t up to the role right out of high school.
Sgt. Angela Hughes was always interested in nursing, but wasn’t up to the role right out of high school.
Instead, she entered the Army as a supply soldier. Though she loved her job, after 15 years, Hughes developed carpal tunnel syndrome and was moved to Fort Hood’s Warrior Transition Brigade to prepare to leave military service.
Hughes is one of several soldiers taking part in a new brigade program to earn nurse’s aide certifications before they transition out of the Army.
The Gateway program runs in coordination with Skillpoint Alliance, an Austin-based nonprofit that provides training and education to job seekers. This is the first time Skillpoint has worked in the Fort Hood area.
On Monday, four brigade soldiers trained at the Hill Country Nursing and Rehab facility in Copperas Cove. The center is where they spent 40 hands-on clinical hours, in addition to the 60 classroom hours needed to earn the certification. The group will graduate from the program on Friday.
“It’s a great opportunity for soldiers who are transitioning ... at no cost to them,” said Anthony Thomas, the brigade transition coordinator. He was contacted by Skillpoint and served as a liaison between the brigade and the nonprofit.
“We try to accommodate soldiers’ career goals through job fairs and workshops,” he said, but this program is the first of its kind for the brigade.
Bethany Paul, Skillpoint’s Gateway program coordinator, worked directly with the students during the four-week training period.
“My job is to get them graduated and employed,” she said. Her organization has an 80 percent employment rate within the first 30 days after students graduate from the program.
Paul’s role required her to select the students and track them throughout the program to ensure successful completion.
“We love being able to serve this population,” she said. “I’m excited to be able to give back.”
Skillpoint also offers mock interviews, resume support and networking opportunities, Paul said.
The brigade soldiers have been pleased with the outcome of the program.
“At the beginning, I was disappointed,” Hughes said of leaving the Army. But now that she’s had time to accept the idea, she is excited to move on and work in nursing.
The patients have been her biggest joy of working at the rehab center.
“The residents are great to be with,” she said. “It’s always something new every day.”
Hughes will exit the Army in May 2014 and is looking forward to spending more time with her three children. “Things slow down a bit when you get out,” she said. She’s glad her post-military life will still require interaction with people on a daily basis.
Resident Eva Xindaris loved working with the brigade soldiers.
“They’re very thorough,” she said. “They’re not rushing.” Though Xindaris is sad to see them go, she knows there will be more in the future.
For Staff Sgt. Jennifer Adams-Ward, working in the facility has been a pleasure.
“It’s a joy to see me put a smile on someone’s face,” she said. She loves to help people, and the residents at the Hill Country Rehab Center have treated her well. “I enjoy learning the story of them and what they’re done in their lives,” she said.
Adams-Ward’s path differs from her fellow classmates. She will not be transitioning out of the Army. She is a medic, currently serving as the medical noncommissioned officer of the brigade’s 1st Battalion. Earning her nurse’s aide certification is one step towards becoming a registered nurse and an Army officer.
At this time, the brigade and Skillpoint are offering an electrician apprenticeship program too. Thomas hopes to add more options in the coming year. The Gateway program is also open to spouses and dependents.
“It’s been very successful,” Thomas said. “I appreciate the fact that they’re giving soldiers this (chance).”
Source: Fort Hood Herald







 Source:
Source: 

