 Healthcare providers recognize the crucial role nutritious diets play in promoting and maintaining good health. People with healthy eating patterns live longer and are at lower risk for serious health problems such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. For people with chronic diseases, healthy eating can help manage these conditions and prevent complications.
Healthcare providers recognize the crucial role nutritious diets play in promoting and maintaining good health. People with healthy eating patterns live longer and are at lower risk for serious health problems such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and obesity. For people with chronic diseases, healthy eating can help manage these conditions and prevent complications.
However, over 30 million people in the U.S. live in food-insecure households – including as many as 9 million children.
Studies have shown that nearly 46% of adults and 56% of children in the U.S. have an overall poor-quality diet and unhealthy diets account for more than $50 billion in U.S. healthcare costs.
The leading grocery technology company in North America, Instacart, wants to help end hunger and reduce diet-related diseases in the U.S.
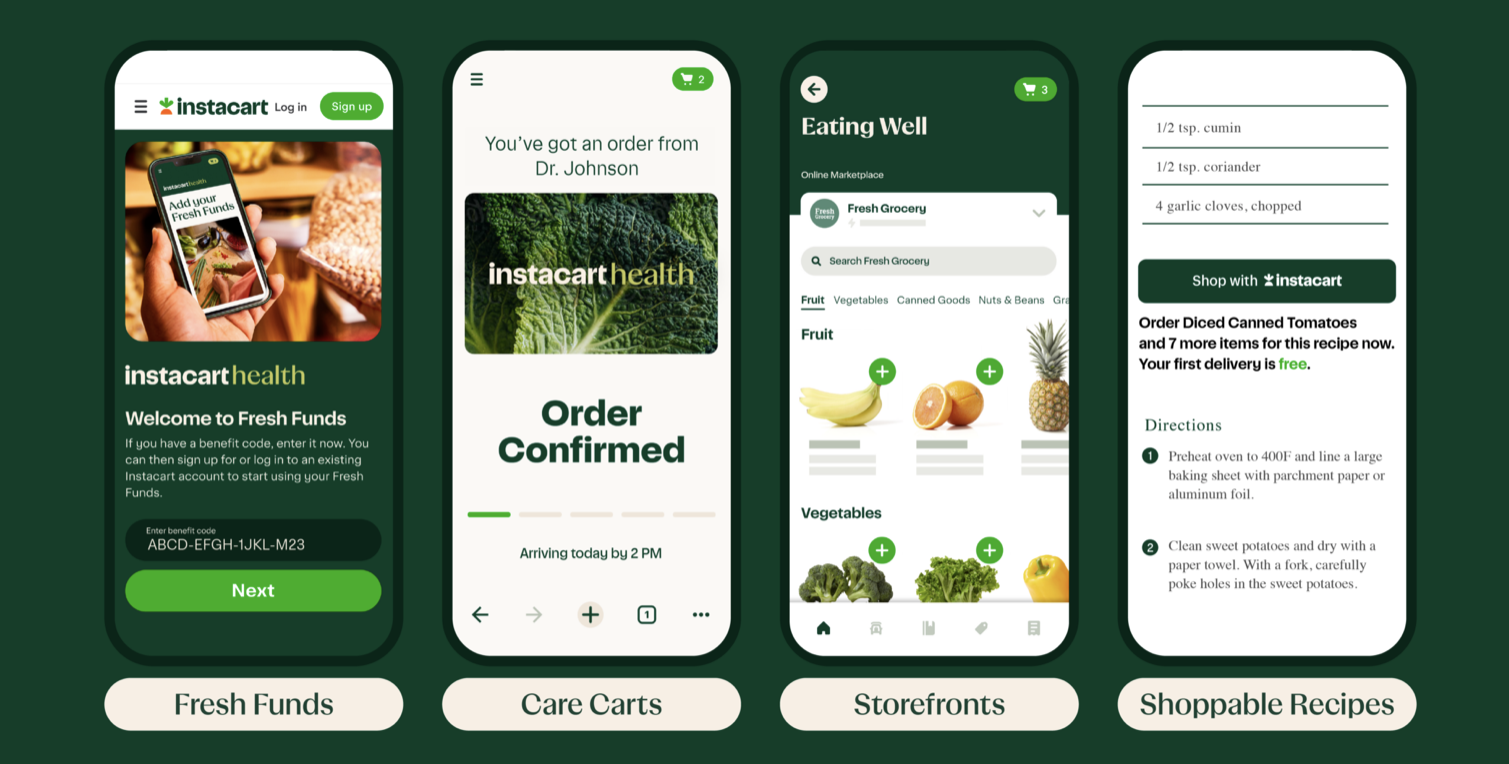
The company announced their release of the Instacart Health’s provider products, designed to enhance collaborative care, promote healthy choices and deliver nutritious foods to patients across the country. Through Instacart Health, they’re giving providers the tools required to build virtual food pharmacies and deliver actionable nutrition advice to their patients through their platform.
"We know that access to nutritious foods can deliver healthier outcomes, but a number of challenges have prevented healthcare providers from effectively adopting food as medicine programs at scale. With Instacart Health, we have the unique opportunity to partner with providers to expand proven nutrition programs and more deeply integrate food as medicine into standard patient care," said Sarah Mastrorocco, Vice President and General Manager of Instacart Health. "We're proud to offer these products to help providers expand access to nutritious food and make medically-tailored groceries and meal advice more actionable. Together, we can help patients and their families take an active role in their health through food."
Boston Children's Hospital is among the first health systems to leverage Instacart Health provider products for its patients, establishing new food as medicine programs to help them get the nourishment they need to manage and maintain their health.
"At Boston Children's Hospital, we're committed to pushing the boundaries of what's possible in pediatric health and addressing our patient health needs holistically," said Dr. John Brownstein, Chief Innovation Officer at Boston Children's Hospital. "Together with Instacart Health, we are excited to explore this technology further to help our providers deliver programs serving patients and families with specific dietary needs. Food and nutrition programs are essential to disease treatment and prevention."
Today, Instacart is available to 95% of U.S. households, including 93% of people living in food deserts. And SNAP participants can use their benefits to shop online from more than 10,000 stores across 49 states and Washington D.C. on the Instacart platform.
"Food desert" is a common phrase used to describe a neighborhood or section of a city where it's hard for people to access healthy food, many of which are low-income communities and communities of color. "Access" is a multi-layered word here — a neighborhood may technically have a grocery store, but it may not be accessible by public transportation.
Instacart partners with more than 1,100 national, regional and local retailers to offer online shopping, delivery and pickup from more than 80,000 stores across North America.
To learn more about Instacart Health visit www.instacart.com/company/health.

 Hospitals are hiring or accepting volunteer teens and young adults as a long-term strategy to help combat shortages in the healthcare industry.
Hospitals are hiring or accepting volunteer teens and young adults as a long-term strategy to help combat shortages in the healthcare industry.  In many cases, patients are now able to access their health care providers through video conferencing, instant messaging, email and other forms of technology. This field, known as telehealth, is growing due to the demand for greater access and convenience in health care, according to
In many cases, patients are now able to access their health care providers through video conferencing, instant messaging, email and other forms of technology. This field, known as telehealth, is growing due to the demand for greater access and convenience in health care, according to  Congresswoman Lois Capps of CA is committed to helping people improve their daily lives through better schools, quality health care, and a cleaner environment.
Congresswoman Lois Capps of CA is committed to helping people improve their daily lives through better schools, quality health care, and a cleaner environment. 



 SEVERAL emergency-room nurses were crying in frustration after their shift ended at a large metropolitan hospital when Molly, who was new to the hospital, walked in. The nurses were scared because their department was so understaffed that they believed their patients — and their nursing licenses — were in danger, and because they knew that when tensions ran high and nurses were spread thin, patients could snap and turn violent.
SEVERAL emergency-room nurses were crying in frustration after their shift ended at a large metropolitan hospital when Molly, who was new to the hospital, walked in. The nurses were scared because their department was so understaffed that they believed their patients — and their nursing licenses — were in danger, and because they knew that when tensions ran high and nurses were spread thin, patients could snap and turn violent.
 With her children grown and husband nearing retirement, Amy Reynolds was ready to leave behind snowy Flagstaff, Ariz., to travel but she wasn't ready to give up her nursing career.
With her children grown and husband nearing retirement, Amy Reynolds was ready to leave behind snowy Flagstaff, Ariz., to travel but she wasn't ready to give up her nursing career.