By Rebecca Riffkin

In 2014, Americans say nurses have the highest honesty and ethical standards. Members of Congress and car salespeople were given the worst ratings among the 11 professions included in this year's poll. Eighty percent of Americans say nurses have "very high" or "high" standards of honesty and ethics, compared with a 7% rating for members of Congress and 8% for car salespeople.
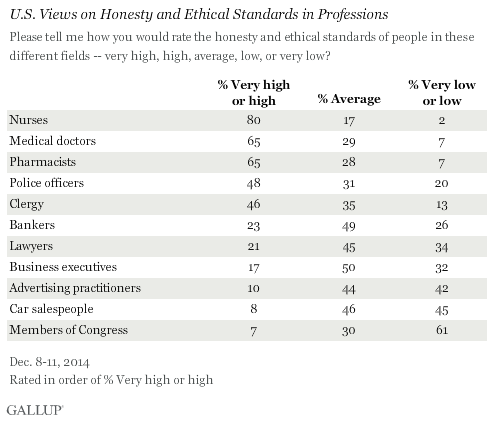
Americans have been asked to rate the honesty and ethics of various professions annually since 1990, and periodically since 1976. Nurses have topped the list each year since they were first included in 1999, with the exception of 2001 when firefighters were included in response to their work during and after the 9/11 attacks. Since 2005, at least 80% of Americans have said nurses have high ethics and honesty. Two other medical professions -- medical doctors and pharmacists -- tie this year for second place at 65%, with police officers and clergy approaching 50%.
Historically, honesty and ethics ratings for members of Congress have generally not been positive, with the highest rating reaching 25% in 2001. Since 2009, Congress has ranked at or near the bottom of the list, usually tied with other poorly viewed professions like car salespeople and -- when they have been included -- lobbyists, telemarketers, HMO managers, stockbrokers and advertising practitioners.
Although members of Congress and car salespeople have similar percentages rating their honesty and ethics as "very high" or "high," members of Congress are much more likely to receive "low" or "very low" ratings (61%), compared with 45% for car salespeople. Last year, 66% of Americans rated Congress' honesty and ethics "low" or "very low," the worst Gallup has measured for any profession historically.
Other relatively poorly rated professions, including advertising practitioners, lawyers, business executives and bankers are more likely to receive "average" than "low" honesty and ethical ratings. So while several of these professions rank about as low as members of Congress in terms of having high ethics, they are less likely than members of Congress to be viewed as having low ethics.
No Professions Improved in Ratings of High Honesty, Ethics Since 2013
Since 2013, all professions either dropped or stayed the same in the percentage of Americans who said they have high honesty and ethics. The only profession to show a small increase was lawyers, and this rise was small (one percentage point) and within the margin of error. The largest drops were among police officers, pharmacists and business executives. But medical doctors, bankers and advertising practitioners also saw drops.

Honesty and ethics ratings of police dropped six percentage points since last year, driven down by many fewer nonwhite Americans saying the police have high honesty and ethical standards. The clergy's 47% rating last year marked the first year that less than 50% of Americans said the clergy had high ethical and honesty standards -- and the current 46% rating is, by one percentage point, the lowest Gallup has measured for that profession to date.
Bottom Line
Americans continue to rate those in medical professions as having higher honesty and ethical standards than those in most other professions. Nurses have consistently been the top-rated profession -- although doctors and pharmacists also receive high ratings, despite the drops since 2013 in the percentage of Americans who say they have high ethics. The high ratings of medical professions this year is significant after the Ebola outbreak which infected a number of medical professionals both in the U.S. and in West Africa.
At the other end of the spectrum, in recent years, members of Congress have sunk to the same depths as car salespeople and advertising practitioners. However, in one respect, Congress is even worse, given the historically high percentages rating its members' honesty and ethics as being "low" or "very low." And although November's midterm elections did produce a significant change in membership for the new Congress that begins in January, there were also major shakeups in the 2006 and 2010 midterm elections with little improvement in the way Americans viewed the members who serve in that institution.
Previously in 2014, Gallup found that Americans continue to have low confidence in banks, and while Americans continue to have confidence in small businesses, big businesses do not earn a lot of confidence. This may be the result of Americans' views that bankers and business executives do not have high honesty and ethical standards, and the fact that their ratings dropped since last year.
Survey Methods
Results for this Gallup poll are based on telephone interviews conducted Dec. 8-11, 2014, with a random sample of 805 adults, aged 18 and older, living in all 50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia. For results based on the total sample of national adults, the margin of sampling error is ±4 percentage points at the 95% confidence level.
Each sample of national adults includes a minimum quota of 50% cellphone respondents and 50% landline respondents, with additional minimum quotas by time zone within region. Landline and cellular telephone numbers are selected using random-digit-dial methods.
Source: www.gallup.com





