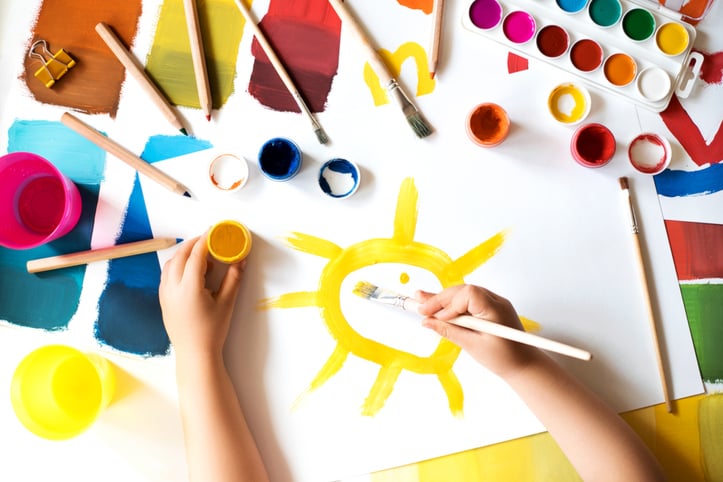
 Art therapy is a growing trend throughout hospitals in the United States. Art therapy is an evidenced-based practice that supports the emotional, physical, social and spiritual well-being of patients of all ages through the therapeutic use of art-making.
Art therapy is a growing trend throughout hospitals in the United States. Art therapy is an evidenced-based practice that supports the emotional, physical, social and spiritual well-being of patients of all ages through the therapeutic use of art-making.
These programs use a wide range of outlets such as drawing, painting, sculpting, collage, and photography as tools to:
- Process feelings about a new diagnosis
- Provide a sense of control through normalizing activities to help them adjust to hospitalization and/or illness
- Cause relaxation and reduction of anxiety
- Rebuild self-esteem
- Help manage pain
- Support groups of patients with similar diagnosis
- Support siblings and family members in caring for their loved one in the hospital
- And more!
Childrens National Hospital uses trained art therapists who offer resources like nature art therapy in the Healing Garden and gallery displays to give children the opportunity to express themselves through creative activities. They are also a Beads of Courage member hospital.
The University of Florida Shands Hospital arts in medicine program started small back in 1990. Jill Sonke, an artist at the hospital said, "No one is suggesting in arts and health that the arts can replace medicine or health care or other therapies or interventions. But the arts have a place in the sphere of whole person care. There's so many ways in which the arts can address things like loneliness and social isolation."
Not every hospital has an in-house art program, many bring in outside help from organizations such as, the Museum of Fine Arts (MFA) or the Caring Arts Foundation Program.
MFA Artful Healing offers art-making activities for children, teens, young adults, and their families in Boston-area hospitals and healthcare centers. The MFA currently provides off-site workshops at Boston Children's Hospital, Massachusetts General Hospital, and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute.
A Parent at Boston Children's Hospital said, "We’ve been here more than ten times in the last two weeks . . . but this is the first time I’ve seen my son smiling. Thank you for that!”
The Caring Arts Foundation Program uses professional photographers to take portraits of patients and their families at Lurie Children’s Hospital. They provide fun wardrobes and props. A common area in the hospital is transformed into a studio with lighting and backdrops. Parents are provided with a full set of photos of their child at no cost — a priceless keepsake. These photo sessions give patients and their families a break from cancer treatment while providing lasting memories.
The use of the arts can help not only patients cope with traumatic events but also hospital staff. For example, immediately after the September 11th terrorist attack, artists were deployed to New York City schools by ArtCares to help children express and address their emotions of having witnessed the horrific event. The same idea can be used for frontline healthcare workers who have experienced trauma throughout the COVID-19 pandemic.
Cedars-Sinai created an art exhibit with artwork made by their employees. Art pieces were made by Nurses, Doctors, Scientists, Pharmacists, Data analysts and more! Many participants were fueled with creativity from their experiences during the pandemic.
John Lange, Manager of Art Curation at Cedars-Sinai said, "A few of them are literal translations of what their experience with COVID-19 was—or maybe it is a painting of a Nurse with their mask on and things like that—while for others, the pandemic was the catalyst for them to start making work for the first time, or to revisit and make more art."
Creating art is just as important as treating patients in an environment filled with art.
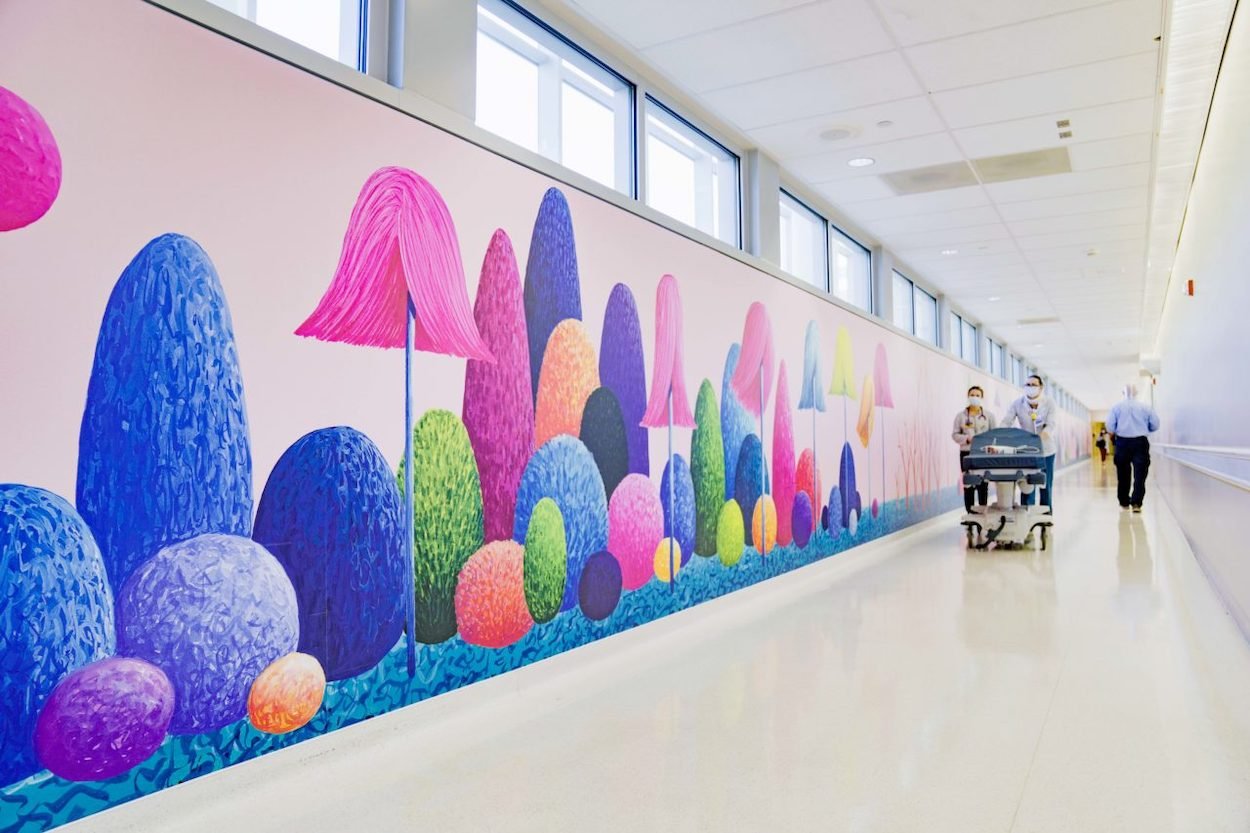
The Children’s Hospital Los Angeles teamed up with the nonprofit RxART to transform their 207-foot-long hallway into a magical forest.
“It’s been a privilege to think about how artwork can make a difference in the context of a children’s hospital. The colorful forest I painted for this long corridor will hopefully do a little to make this experience a bit more tolerable," said Swiss artist Nicolas Party.
With all of the positive effects art has on mental health and cognitive functions, we are excited to see more health systems implementing these types of art programs.


 There are large disparities in mental healthcare across races and ethnicities in the U.S. Many factors contribute to the poor mental health outcomes of minority populations. Such as:
There are large disparities in mental healthcare across races and ethnicities in the U.S. Many factors contribute to the poor mental health outcomes of minority populations. Such as: Even before the pandemic, healthcare providers experienced burnout and other negative mental health issues. Now more than ever, it is critical health systems take steps to support their staff's well-being.
Even before the pandemic, healthcare providers experienced burnout and other negative mental health issues. Now more than ever, it is critical health systems take steps to support their staff's well-being. Hospitals are seeing more cases of severe depression and suicidal thoughts among children, particularly attempts to overdose.
Hospitals are seeing more cases of severe depression and suicidal thoughts among children, particularly attempts to overdose.  Before the COVID-19 pandemic, Nursing was known to be a stressful profession. There was plenty of
Before the COVID-19 pandemic, Nursing was known to be a stressful profession. There was plenty of  Putrino said, "Listen, what we need is a space or a series of spaces where our healthcare workers can sit down and for just a moment have a lot of their stress just relieved and taken away from them."
Putrino said, "Listen, what we need is a space or a series of spaces where our healthcare workers can sit down and for just a moment have a lot of their stress just relieved and taken away from them." Ohio State University Medical Center (OSUMC) Stress, Trauma and Resilience (STAR) Program uses the Buckeye Paws
Ohio State University Medical Center (OSUMC) Stress, Trauma and Resilience (STAR) Program uses the Buckeye Paws 
 Many Nurses and Doctors said in interviews with
Many Nurses and Doctors said in interviews with  Approximately 56 million American adults are struggling with a mental illness or substance use disorder, according to the
Approximately 56 million American adults are struggling with a mental illness or substance use disorder, according to the 
 Mental health conditions do not discriminate based on race, color, gender or identity. Anyone can experience the challenges of mental illness regardless of their background. However, background and identity can make access to mental health treatment much more difficult.
Mental health conditions do not discriminate based on race, color, gender or identity. Anyone can experience the challenges of mental illness regardless of their background. However, background and identity can make access to mental health treatment much more difficult.
 There are just a handful of psychiatrists in all of western Nebraska, a vast expanse of farmland and cattle ranches. So when Murlene Osburn, a cattle rancher turned psychiatric nurse, finished her graduate degree, she thought starting a practice in this tiny village of tumbleweeds and farm equipment dealerships would be easy.
There are just a handful of psychiatrists in all of western Nebraska, a vast expanse of farmland and cattle ranches. So when Murlene Osburn, a cattle rancher turned psychiatric nurse, finished her graduate degree, she thought starting a practice in this tiny village of tumbleweeds and farm equipment dealerships would be easy. It may surprise fans of Johanna Basford’s intricately hand-drawn coloring books that the artist is, by her own admission, “pretty bad” at coloring.
It may surprise fans of Johanna Basford’s intricately hand-drawn coloring books that the artist is, by her own admission, “pretty bad” at coloring.