
With maternal mortality and morbidity rates that are worse than any other developing country in the world, America’s need for more diverse and culturally-conscious health care providers is urgent.
Many nursing institutions preach “diversity,” but schools like Frontier Nursing University (FNU) are achieving it through programming, initiatives and partnerships with like-minded organizations.
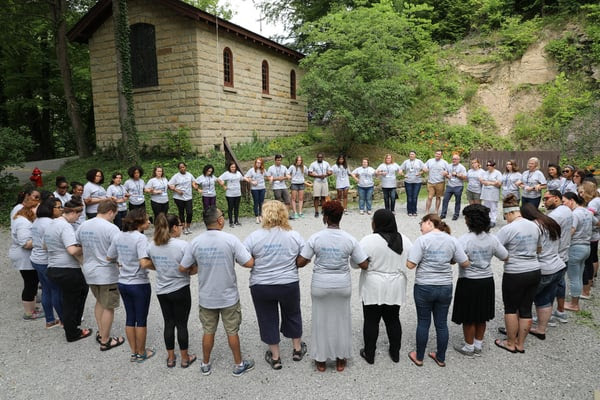
Each year, FNU hosts its Diversity Impact Student Conference. In its eighth year, the conference is hosted by students and faculty leaders in FNU’s PRIDE Program, which was established to promote recruitment and retention to increase diversity in Nurse-Midwifery and Nurse Practitioner education.
FNU has put the “impact” in Diversity Impact, especially in this year’s event. With a theme entitled “We Are One: Uniting Dreamers with Diverse Voices,” presenters at this year’s four-day conference spoke on mental health and cultural care, transcultural nursing and the current state of mortality rates in the African American community.
Each student who attended was given opportunity to not only listen to an impactful keynote, but also to participate in a culturally eye-opening field trip, cross-cultural communication exercise, and collaborative discussions to improve minority health among underrepresented and marginalized groups.

These powerful conversations ranged in topic from environmentally-sustainable healthcare to mental health in patient and police interactions, to vulnerable populations and sexual IQ risk reduction. Each year at Diversity Impact, attendees walk away with proactive solutions to create meaningful connections and provide better care within diverse communities.
In addition to its annual event, FNU partnered with the Association of Women’s Health, Obstetric and Neonatal Nurses (AWHONN) in a brand new initiative this year to produce a video about the need for a diverse nurse-midwifery workforce to improve health outcomes across the United States.
This five-minute video, filmed as part of AWHONN’s “Partners in Care" program, highlights how Frontier Nursing University students are providing significant contributions to address health disparities for women who are facing language, racial, geographical and other socioeconomic barriers.
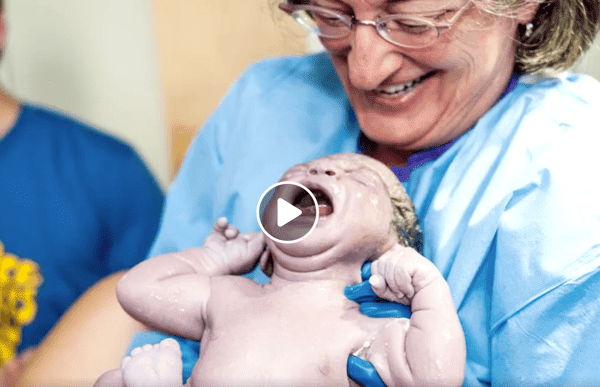
“The fact that African American women are 3 to 4 times more likely to die in and around childbirth than their white counterparts - that struck a chord with me,” said Ameenah Jackson, FNU nurse-midwifery student, in the video.
Jackson, along with hundreds of other FNU students, is the future of quality care for women who, before now, have not felt heard or valued by a health care provider.
A portion of the video is an interview with a new member of FNU’s Executive Leadership Team. Dr. Maria Valentin-Welch, DNP, MPH, CDP, CNM, FACNM, was brought on board in September 2017 as the inaugural Chief Diversity and Inclusion Officer (CDIO).
Valentin-Welch’s position is designed to guide FNU on matters of equity, diversity and inclusion. Together with the president, dean, chief operations officer, chief advancement officer, and executive vice president for finance and facilities, the CDIO will lead the development of a vision and strategy that champions the importance of a diverse and inclusive environment that values and supports all members of the University community.
With over 30 years of teaching experience, Dr. Valentin-Welch is working from the classroom outward in strategizing diversity initiatives for FNU.
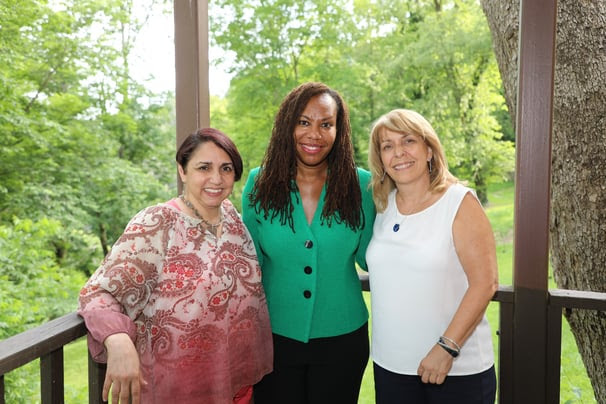

“The strategies that I feel will have the most positive impact on Frontier are building these excellent student services, as well as diversity and inclusion training strategies and tactics to enhance our courses by threading diversity and inclusion issues along the way,” said Dr. Valentin-Welch. “We want to thread the subject matter even further throughout the curriculum. We will be stronger individually and as a whole because of the introductions of these plans.”
The AWHONN reporter concludes: “FNU is at the forefront of tackling the difficult and delicate issues related to equity of care through head-on conversations and diversity events for students.”
One such conversation was had in June 2018 between FNU President Dr. Susan Stone, DNSc, CNM, FACNM, FAAN, certified nurse-midwife, and President of the American College of Nurse-Midwives (ACNM) and Andrew Bennie, Product Director at Springer Publishing Group and guest host of the weekly “Nursecast” podcast series.
Dr. Stone and Bennie’s discussion tackled the question: “Why is Maternal Mortality Growing in the United States?” In the eighteen minute podcast, Dr. Stone pinpoints a lack of racially-concordant care as a culprit.
According to data, 700 women around the U.S. die of pregnancy complications per year, while 50,000 cases are near misses. Many of those cases are disproportionately correlated to race.
Dr. Stone explains that patients are more receptive to care from a health provider who understands their culture and socioeconomic background. Currently, only 6% of midwives in the United States are women or men of color. FNU’s initiative is to diversify not only the field of midwifery, but the healthcare workforce as a whole.
“Today about 22% of FNU students are men and women of color – up from just 9% in 2010,” said Dr. Stone.

Each population in America’s melting pot, formed by race, socioeconomic status, sexual orientation, language, or a combination of other factors, will see better health outcomes with culturally-concordant healthcare providers and models. Institutions like Frontier Nursing University are equipping and encouraging their students to answer the call to make these underrepresented populations feel heard, valued and served.
About Frontier Nursing University:
The mission of FNU is to provide accessible nurse-midwifery and nurse practitioner education to prepare competent, entrepreneurial, ethical, and compassionate leaders in primary care to serve all individuals with an emphasis on women and families in diverse, rural, and underserved populations. FNU offers graduate Nurse-Midwifery and Nurse-Practitioner distance education programs that can be pursued full- or part-time with the student’s home community serving as the classroom. Degrees and options offered include Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP), Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) or Post-Graduate Certificates. To learn more about FNU and the programs and degrees offered, please visit Frontier.edu.







 Diversity in the Nursing field is necessary to progress health equity and improve patient outcomes. As a result of efforts in recent years, the Nursing workforce today is more diverse than it was a decade ago, but there is still work to be done. The goal is to have a health workforce that mirrors the nation’s diverse population.
Diversity in the Nursing field is necessary to progress health equity and improve patient outcomes. As a result of efforts in recent years, the Nursing workforce today is more diverse than it was a decade ago, but there is still work to be done. The goal is to have a health workforce that mirrors the nation’s diverse population. Even though women comprise an estimated
Even though women comprise an estimated 
 Unique challenges encompass the delivery of quality healthcare in the entire world as a whole. People of all ages are terminally ill -- with approximately half the American population fighting hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, arthritis and mental related illness.
Unique challenges encompass the delivery of quality healthcare in the entire world as a whole. People of all ages are terminally ill -- with approximately half the American population fighting hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, arthritis and mental related illness.





.jpg)



